With the rapid development of Internet of Things technology, RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology, as a non-contact automatic identification technology, has been widely used in various fields. RFID system is mainly composed of electronic tag, reader and antenna three parts, of which the antenna as a bridge between the reader and the electronic tag, its performance plays a crucial role in the stability and reliability of the entire RFID system. This article will take you through the performance of RFID reader antennas and how to choose the right RFID reader antenna.

The basic function of RFID reader antenna
The main function of the RFID reader antenna is to transmit and receive RF signals. When the electronic tag enters the working range of the reader antenna, the antenna will emit a RF signal of a certain frequency to activate the electronic tag and receive the returned information. This process may seem simple, but it actually involves complex electromagnetic wave transmission and signal processing techniques.
Key performance parameters of RFID reader antenna
1. Frequency
The working frequency of RFID antenna is one of its most important parameters. RFID systems with different frequencies are suitable for different application scenarios. Common RFID frequencies include low frequency (LF, such as 125kHz), high frequency (HF, such as 13.56MHz) and ultra-high frequency (UHF, such as 860-960MHz). The choice of frequency directly affects the reading and writing distance, penetration ability and anti-interference ability of the antenna.
2. Gain
Gain is an important indicator of antenna performance, which indicates the ability of the antenna to convert input power into radiated power. The higher the gain, the greater the transmitting range of the antenna, and the further the read and write distance. Common RFID antenna gain values include 3dBi, 6dBi, 8dBi, 12dBi, and so on.
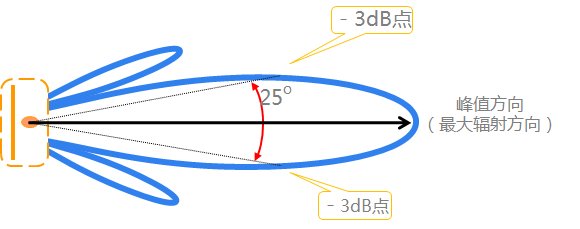
3. Beam width
The beam width determines the antenna's coverage and resolution. Generally speaking, the larger the gain of the antenna, the narrower the beamwidth, the more concentrated the coverage area; Conversely, antennas with smaller gain have wider beamwidths and wider coverage.
Antenna lobe width
4. Impedance matching
Impedance matching is the key to ensure antenna performance. The impedance between the antenna and the reader must be matched to reduce signal reflection and loss. In practical applications, impedance matching is usually achieved by adjusting the size, shape and material of the antenna.
5. Polarization mode
The polarization mode is divided into linear polarization, circular polarization and elliptical polarization. The polarization mode of the RFID reader antenna needs to match the polarization mode of the electronic tag to ensure the effective transmission of the signal. The linearly polarized antenna is suitable for the application scenario where the polarization direction is fixed, while the circularly polarized antenna is suitable for the application scenario where the polarization direction is uncertain or changes.
Performance impact of RFID reader antenna
1. Read and write distance
The gain and frequency of the antenna directly affect the read and write distance of the RFID system. The higher the gain, the farther the read/write distance. At the same time, high-frequency and UHF antennas usually have longer read and write distances
2, anti-interference ability
RFID systems may be affected by various sources of interference in practical applications, such as metal objects, liquids, and other electromagnetic signals. Excellent antenna design should have good anti-interference ability to ensure the stability and reliability of signal transmission.
3. Penetration ability
In some application scenarios, such as logistics warehousing and intelligent manufacturing, RFID systems need to penetrate obstacles (such as cardboard boxes, metal shelves, etc.) to read electronic label information. At this time, the penetration ability of the antenna becomes one of the key factors.
4. System stability
The stability of the RFID system depends not only on the performance of the antenna, but also on the design of the reader, the quality of the electronic tag, and the integration of the entire system. However, as the key link of signal transmission, the stability and reliability of antenna performance have an important impact on the stability of the whole system.
In an RFID system, choosing the right reader antenna is a key step to ensure the efficient and stable operation of the system. This process not only needs to consider the performance indicators of the antenna, but also needs to be combined with the specific requirements of the actual application scenario for comprehensive analysis. The following will explain in detail how to choose the right RFID reader antenna, and combined with practical application cases to explain.
Case 1: Logistics warehousing management
In logistics warehousing management, RFID systems are used to achieve rapid warehousing, warehousing and inventory of goods. Due to the large warehouse area, high cargo accumulation, and obstacles such as multi-layer packaging and metal shelves, the remote reading and writing ability and anti-interference ability should be considered when selecting the antenna.
Selection strategy: Use ultra-high frequency (UHF) antenna, which has higher gain and longer read and write distance; At the same time, selecting an antenna design with good anti-interference ability can stably identify multi-layer packaging and accurately read electronic label information without interference from metal shelves.

Case 2: Manufacturing line tracking
In the manufacturing industry, RFID technology is used for material tracking and process management on the production line. Because the materials and workpieces on the production line are in a high-speed moving state, and may go through multiple processes and stations, the RFID reader antenna is required to have high-speed mobile identification and long-distance reading and writing ability.
Selection strategy: The manufacturing industry will choose UHF antennas, combined with directional antenna design to improve recognition accuracy and read and write distance. At the same time, considering the complexity and variability of the production line environment (such as metal equipment, electromagnetic interference, etc.), antenna products with excellent anti-interference ability and stable performance will be selected.
Case 3: Library management
In the library, RFID technology is used for book lending, return and inventory management. In order to achieve rapid identification and tracking of books, the library will install RFID reader antennas at the circulation desk, book return boxes and shelves.
Selection strategy: The library will choose high-frequency or UHF antennas, because these two frequencies have better penetration and anti-interference ability in the library management scene. At the same time, considering the particularity of the library environment (such as dense books, limited space, etc.), antenna products that are small, easy to install and can cover multiple shelf areas will be selected.
As an important part of RFID system, the performance of RFID reader antenna directly affects the stability and reliability of the whole system. By understanding the key performance parameters and influencing factors of the antenna, we can better choose the appropriate antenna products to meet the needs of different application scenarios. With the continuous development of Internet of Things technology, RFID technology will be applied and expanded in more fields, bringing more convenience and benefits to our life and work.